
I know I need SEO, but I don’t know exactly what I need.
We have heard this statement several times. Entrepreneurs realize the value of SEO, but they don’t truly know how to do it for their e-commerce business.
Before embarking on optimizing on page SEO for ecommerce, it’s crucial to understand what you hope to gain.
In this article, you’ll learn about the following:
- Understanding your SEO needs so you can focus on the most profitable areas
- How SEO really works for E-Commerce Websites
- Our 8 step technical On-Page SEO process to guarantee you more traffic.
- Our 7 Step On-Page SEO guide to user experience and engagement
Most users prefer using Google because it returns the most relevant search results on the web – and by ‘users’, we mean your potential customers. This means that being ranked on the top pages allows online stores to receive more visitors and generate more leads.
So, how can you rank higher than your competitors on Google?
The answer is a well-rounded website. Whether you’re just getting started with a new online store, or improving an existing site, you need to step up your SEO game.
I. Understanding your SEO needs

SEO can help potential customers find your store in search results. Let’s say someone is looking for a product you’re selling. How can we make Google recommend your brand to that user, instead of another store? This is where SEO can help.
A. Business Goals
Your business goals should always come first. Do you want to increase conversion? Build brand or product awareness? If your business goals are clearly set, it will be easier to determine the SEO strategy that will best fit your needs.
B. Existing Performance
Look at your analytics data to assess the existing performance of your site. It will show your site’s traffic and conversion trends over the years, helping you understand what keywords you need to optimize for. We will show you exactly how to do keyword research shortly.
C. Resource Constraints
After looking at your analytics data, and knowing where you’re lacking, you’ll know how to fill in the gaps. Know where you need help, and it will make the SEO planning easier.
II. SEO Basics for E-commerce Websites

For an e-commerce site, driving relevant traffic to boost sales is crucial.
It’s critical for websites to appear on Page 1 of Google. Surprisingly, the top three organic positions alone receive 58.4 percent of all clicks from users.

Websites ranked number one received an average click-through rate of 36.4 percent. The second spot received a CTR of 12.5 percent, and number three had a share of 9.5 percent.
Do you want to know how to rank your e-commerce site? Read on.
A. Start your Research
On-page SEO work needs two types of research: Keyword and Competitor Research.
The primary objective of doing research is to identify the gaps between your site, and the sites that are doing better. Keep in mind that the market you are about to enter might already be well-served by savvy site owners.
1. Keyword Research
First of all, targeting the wrong keywords makes your campaign ineffective. It can lead to low quality traffic, and few conversions.
Go for keywords that are highly relevant to your brand or products. What terms are your ideal clients using when searching for your service?
You can use tools such as:
Google Keyword Planner (formerly the Keyword Tool)
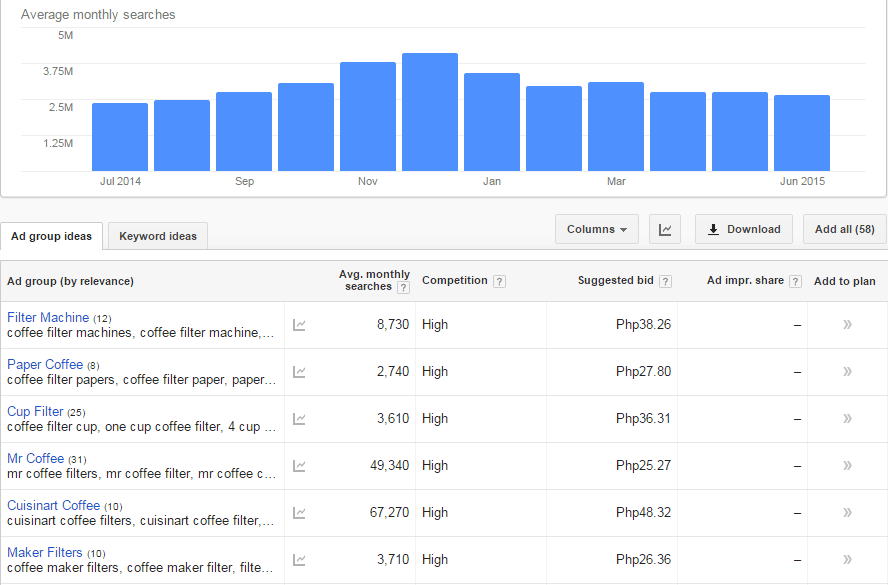
Übersuggest
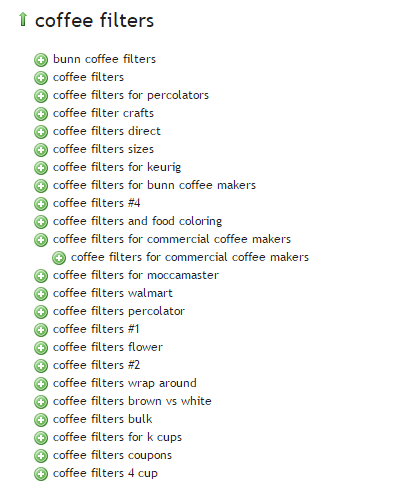
2. Competitor Research
Insightful competitor analysis
Insightful competitor analysis is an essential strategy to find out what rival e-commerce firms are doing. In SEO, you can track and analyze the performance of your competitors in relatively simple ways.
Which keywords are your main competitors going for?
List down the keywords which your competitors appear to be using with their SEO strategy. Check if they have higher Domain Authority and Page Authorities than you.
- Domain Authority is a calculated metric for how well a given domain is likely to rank in Google’s search results. It is used to compare one site to another, or to track the strength of your website over time. It is scored on a 100-point, logarithmic scale.
- Page Authority is a calculated metric for how well a given webpage is likely to rank in Google’s search results. It is also scored on a 100-point, logarithmic scale, and used to predict how well a specific page will rank on search engines.
If your competitors have higher DA’s or PA’s than you, contending against them will be very difficult. So, it may be a good idea to focus on other keywords or “longer tail” keywords instead.
You can use these tools to determine DA’s and PA’s:
Allows for checking the SEO title and description your competitors use in their title tags.
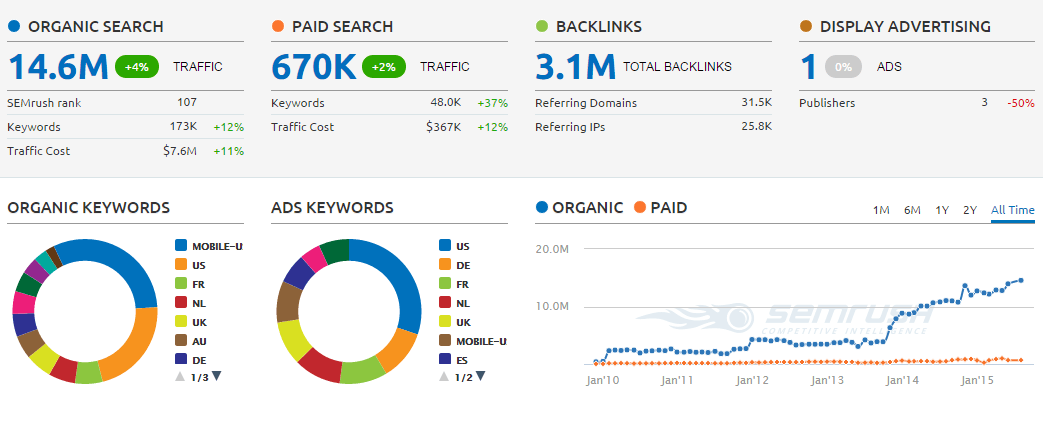
Allows for seeing what keywords your competitors are ranking for on both organic and paid search.
What is their site architecture like?
Try to look at the site architecture of competing sites, or the biggest companies in your industry. Pay special attention to popular products in a particular category, related products, top rated products, and recently viewed products.
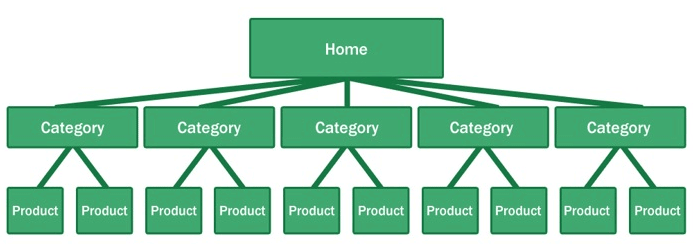
Here’s why your site architecture is essential for organic traffic:
- Google considers your site’s homepage the most authoritative page, so content closest to the homepage receives the most value.
- By structuring your e-commerce store correctly, your main level navigation pages, such as the category pages, will contain a majority of your site’s authority.
- Adding relevant, high-quality content to your main level navigation pages can increase conversion, page authority, and sub-category page’s authority.
B. Identify Current Problems
After discovering what keywords are going to make you the most profit comes auditing your site for problems.

1. Find site errors
Here are the top errors you’ll want to correct:
- Redirecting any 404 pages to actual content
- Changing 302 redirects to 301 redirects
- Updating duplicate content pages, meta titles, and meta descriptions
The above mentioned are called HTTP status codes. These are three-digit numbers returned by servers that indicate the status of a web element.
404 HTTP status code
It can be shown as 404 Error, 404 Not Found, Error 404, 404 File or Directory Not Found, etc. This status code means that the server has not found anything matching the Request-URL. Or, simply the page you were trying to reach on a site couldn’t be found on their server, has been removed or does not exist.
Having lots of 404 pages will hurt your site in many ways. For instance, if a ranking page resolves to a 404 error, it might frustrate the user. This means you will be throwing away some earning potential. Google also counts it as a poor user experience. If you don’t fix the errors, Google will eventually remove that page from their index, which will eventually hurt your overall rankings.
302 Redirect HTTP status code
It’s also known as a temporary redirect. 302 should be put in place if you want to redirect visitors into another webpage, but you plan to bring the redirected page back after some time.
It’s not really recommended since it can hurt your site’s search engine visibility. While the redirected page will retain its page authority and traffic value, the temporary page won’t accumulate any. It’s often used to test a new page. You can gain client feedback without affecting the old page’s ranking.
301 Redirect HTTP status code
This refers to a permanent redirect from one URL to the other. All qualities of the redirected page will be passed on to the detour page. A 301 redirect is often implemented if one is ready to make a test page permanent. The old page will be removed from Google’s index, and the new one will replace it.
Without 301 redirect, the web authority which your previous domain collected will be thrown right out the window. Any inbound links earned will be lost, and you won’t get any SEO credit.
There are dozens of free online services that are capable of checking your website for errors, and finding ways of improving your web page.
Google Webmaster Tools, for instance, can help you identify any page or links with errors, scan for malware, find pages with short or missing titles, find duplicate meta tags, and much more.
2. Determine your site speed
Any delay is enough reason to make your customers leave. This converts to lost revenue, which can hurt your bottom-line.
One study revealed that 1 in 2 visitors will abandon a website that takes more than 6 seconds to load.
There are various tools to help you check your loading speed:
- Yahoo! Y slow
- Google Page Speed
- Pingdom is the quickest and easiest one
For a more in-depth guide to how to speed up your site see our article here.
C. On-Page Optimization
On-page optimization includes all of the actions you take within your own web pages to help your site rank better.
Learn more about on-page optimization for your online store on the next step.
III. Optimizing On-page SEO Technical Factors

If your online store is not optimized for both search engines and users, you have a small chance for success. On-Page SEO refers to the settings you can apply on the website so that it is optimized for search engines.
A. Why start with On-page SEO?
- With On-Page SEO, you ‘speak’ the language of search engines. You can easily make them understand what your website is about.
- On-Page SEO can make the users happy. It ensures that your website is setup correctly, which leads to a better user experience.
- Before promoting your site through off-page SEO, you need to be sure that the website is optimized and is running smoothly.
If you don’t know the basics of on-page SEO, you have very little chance of securing top spots for competitive key phrases. Get it right and you’ll succeed on the search engines.
Here are the basic factors of on-page SEO:
1. Title Tag
Title tags or title elements define the title of a document. It should be an accurate and concise description of a page’s content.
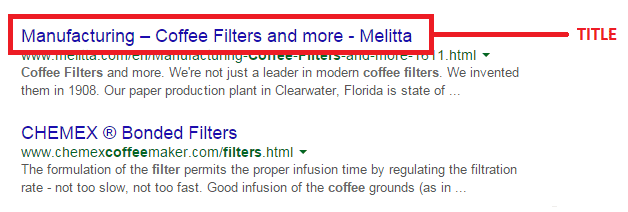
Place your main keyword and variations in the title tag of a page. Google would display around 70 characters of a title tag, or based on pixel width. You can preview how your title tags will appear like through Moz’s preview tool. Make sure to include your business name along with the main keyword phrase you are targeting.
2. Title Tag Optimization
Your site’s title has to be appealing enough for a user to want to find out more information.
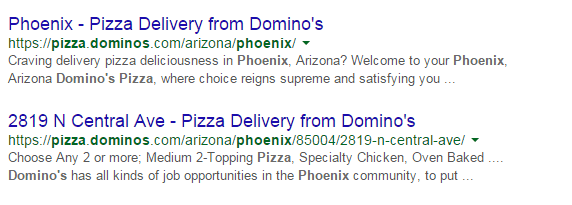
Things to include in your title:
- Business Name: Aside from customers may search you by your brand name, it’s also important for breading purposes. In the example above, it’s Domino’s.
- Keywords: Putting certain keywords in your title can help them rank, just don’t staff too many. Domino’s used ‘pizza delivery’.
- Toll-free numbers: It helps your visitors to take a direct action, and makes your title look professional. Users are left with an impression of authenticity of the business.
B. Meta Descriptions
A meta description is the snippet of information below the link of a search result. It describes the contents of the page to the searcher, with the goal of convincing the searcher to click through to your website.
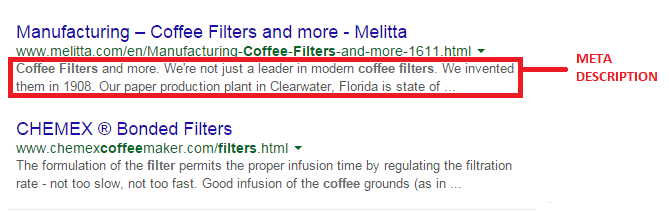
They may not contribute as a ranking signal but meta descriptions can encourage people to want to visit your website. It describes your business and shows up in the search results page beneath the title tag. It should be well-written and approximately 156 characters.
Think of meta description as a sales pitch for what the landing page is about. Get practical instructions on how to update them using WooCommerce.
1. Meta Tags Optimization
As mentioned earlier, meta description is something that when done properly can urge users to check out your website.
Things to include in your Meta Description:
- Selling Point: To get some advantage, write what your customers want to hear. For instance, a phrase like ‘affordable, all-natural coffee filters from only $3.99’ may result in more clicks.
- Keywords: It will give you some advantage in Google’s relevancy algorithm.
- Toll Free Numbers: If you don’t want to place it in your title tag, include it in your meta description instead. Again, it may help your visitors to take a direct action.
C. Heading Tags
Use headings correctly without over-optimizing them. Your main keyword should be in a H1 tag. Split sub-headings up with H2 and H3 tags. Only use the H1 tag once, and others can be used multiple times.
For more information of the correct use of when and how to use heading tags, check out How To Use H1-H6 HTML Elements Properly.
1. HTML Tags Optimization
The text inside your header tags is given very high importance by the search engine. They highlight certain parts of your website.
Header 1: Use it to define the most important section of your page. The H1 tag is an influential ranking factor, and an important signal to search engines as to what a page of content is about.
Header 2: Use it for sub-titles or important sections of your pages.
D. Content
Your content should be written primarily for users, and secondly for search engines. Make sure that the content on your homepage helps visitors learn more about your business, and the products you’re offering.
Use the keywords from your research, but make it look as natural as possible and easy to understand for the user.
Again, don’t forget to use H tags to break up your content into easy to digest sections.
E. URL Structure
Which has a more search engine friendly URL structure: “www.domain.com/page-name/” or “www.domain.com/index.php?id=1?” Obviously, the former makes more sense to both users and search engines.
Avoid having main pages sit too many directories deep in your site. Use hyphens rather than underscores. If you do make changes, implement 301 redirects from the old URL to the new. This way, your users won’t have to face 404 pages.
F. Keyword Optimization
Keyword stuffing is no longer acceptable. Maintain a balance between your keywords and your content.
1. Elements of Keyword Optimization:
- Keyword Density: In SEO, keyword density is the measurement in percentage of the number of times a particular keyword or phrase appears compared to the total number of words in a page. It’s also an indicator whether your page is relevant to the targeted keyword. Yoast SEO plugin can help analyze keyword density.
- Related Keywords: Related keywords are keywords of industries and markets that are closely or somehow related to your niche. It’s using related, but less obvious keywords to bring targeted, conversion-friendly traffic. LSI is smart enough to see ‘coffee filters’ is somehow closely related to tea and accessories for brewing. LSI Graph is a good tool to find LSI keywords.
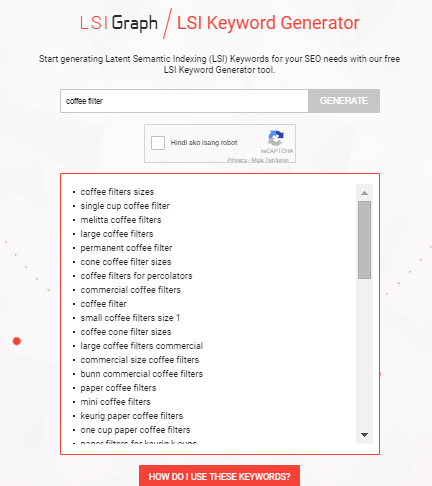
- Long Tail Keywords: These are longer and more specific keyword phrases that visitors are more likely to use. It’s about adding common words like ‘best’, ‘free’, ‘cheap’, or ‘top’ to your actual keywords. Long tail keywords can help you craft the kind of content that engages and inspires readers.
Long tail keywords have less competition, give more qualified leads, and improve head term rankings. According to a research by Statistica, 50% of your focus should be on long-tail keywords in order to achieve a successful On-page SEO.
G. Internal Link Optimization
Internal linking is when you link pages of your website to other pages within your website. It’s a process that involves optimizing internal links, in order for algorithms to determine the relevance of web page content.
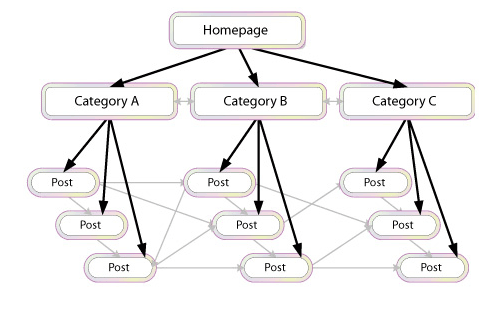
If you lack internal links, it will be difficult for Google to crawl and index deeper sections of your website.
1. Why are internal links important?
- Internal links improve your ‘link flow’ or page rank to individual pages on your site, helping them to rank better.
- The anchor text of links helps Google to understand the context of a webpage, and to rank better.
- Anchor text: It’s what you call the clickable text in a hyperlink. A good anchor text includes the appropriate keyword to give the page it is linking to more relevant meaning.
- Internal links help Google Bots crawl and access different parts of your site, and also improve user experience.
H. Image Optimization
On-page images need to be optimized because search engines can’t read them. This means the web crawlers would only read the text.
1. Elements of Image Optimization:
- Alt text: Try to move the mouse over an image on a website. If a short description appears, that is alternate text. You can use your relevant keywords as ALT text.
- File name: Use meaningful file names for your images, such as ‘coffee-filter-basket.jpg’ instead of just ‘DSC1234.jpg’. Make sure the file name is relevant to the image.
IV. Optimizing On-Page SEO for User Experience and Engagement.

Google has been updating its ranking factors consistently, and user experience and engagement have become one of them, especially for mobile. What links UX and SEO? It’s about attracting visitors and converting them into customers.
Once you create a great user experience, visitors would perceive your site positively which encourages sharing, return visits, bookmarking, and inbound links. These factors are signals recognized by the search engines, contributing to high rankings.
- Focus on designs that fit SEO principles – you need to maximize H1 and H2 titles, optimize menu names and functionalities, create a clear navigation path, and provide focused product names and descriptions.
- Call-to-action – CTA buttons or even links with CTA should be designed not only for user experience, but also linked to content and page elements optimized for SEO.
- Focus on quality – when talking about quality websites, user experience is also taken into account page speed, easy navigation, internal link structure, descriptive content, and page layout.
A. Engagement Metrics
As a search engine delivers a page of results to you, it observes how you engage with those results, measuring the success of the rankings in the process. Search engines are looking for that ‘long click’, wherein a user does not immediately return to the search page.
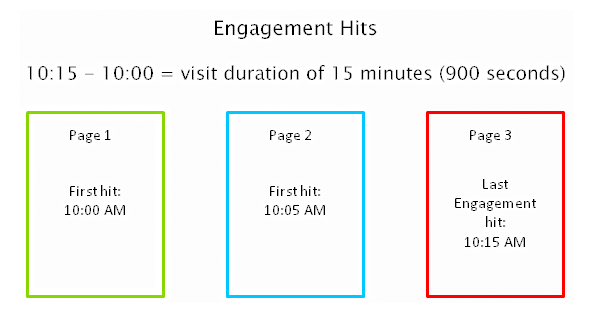
For instance, you click on the first link found on the SERP, then immediately hit the back button and clicked the second link. The search engine will interpret this as not being satisfied with the first result.
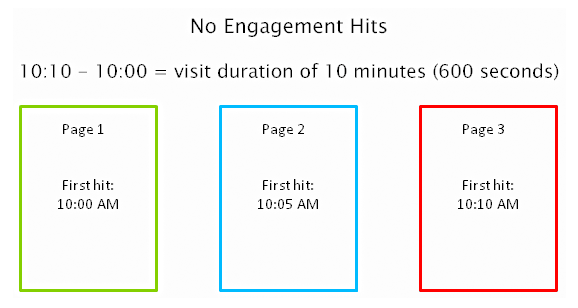
1. How important is Time on Site?
Time on site or visit duration refers to how long a visitor stays on your website. Because Google wants to give their users the best experience, they actively measure user behavior to help shape their algorithm. If a user is spending a significant time on a site, interacting with it, and going deeper within the content, it means there is something of value on the site for that particular user.
2. What is Relevance?
The relevance of a website’s content is particularly important for search engines. The term ‘relevance’ describes the extent to which the content of a website corresponds to the search term used. It can affect a website’s ranking in the search results, for a given search term.
If you’re selling coffee filters, you must not go off topic and talk about juicing machines. Go for the search terms that your potential customers are searching for. “Disposable paper coffee filters” could be a good choice for a keyword for a coffee-filter vendor, but “coffee maker parts” might not work. You would be confusing yourself, your to-be customers, and the search engines. Your relevance would get hurt, hence you ranking would get hurt too.
Ask yourself, how relevant is your page content to the keyword query of your visitor? You can make your site more relevant to searchers by optimizing the different on-page factors discussed in Part III. They include your site’s meta tags, headings, body text, and other content.
3. Google will reward you for being relevant.
According to Google’s official blog, their goal is simple: to give people the most relevant answers to their queries as quickly as possible.

Maintaining your site’s relevance may lead to more clicks, and a higher position in search results. When Google changed its algorithm last February 2011, they began promoting sites with reports, in-depth analyses, and other forms of high-quality, value-adding content. Sites that were deemed irrelevant and invaluable by the algorithm were demoted.
4. How Google determines relevance?
Google displays web pages in their search results based on the authority and relevance of the page. So, how does it determine relevance? According to Neil Patel, it analyzes a page’s content based on several factors, including where and how often you use certain words in that piece of content. You can check out Google’s other ranking factors here.
Let’s move on to your WooCommerce product page.
B. Important Elements for On-Page Optimization
These are the elements that are important for on-page optimization:
1. Customer Reviews
These reviews not only improve your business, they also provide an amazing source of unique content. Internet Retailer reveals that an online store can increase its e-commerce conversion rate by 14-76% by adding product reviews.
Search engine spiders like unique content that is regularly updated, and user reviews are a great way to create more of this on your website. According to data, 88% of consumers trust online reviews as much as personal recommendations. This means that potential customers will be searching for the name of the product plus the word ‘review’, or related words such as ‘ratings’.
Compare these two images on SERPs:
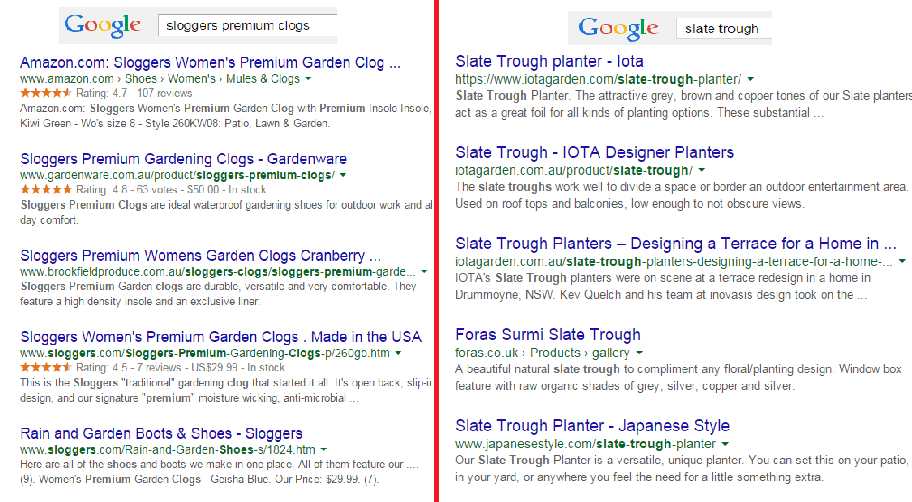
The organic search results on the left are showing ratings just above the meta tag, while the image on the right doesn’t. So, what determines if ratings are shown on SERPs?
Apparently, sites on the left are using schema markup on their reviews. That is why their ratings occur on SERPs.
In AdWords, they are enabled through the product reviews ad extension. You have to submit your product data to Google, and be a client of selected review websites. Get reviewed by at least 30 unique users, submit your reviews to Google, and have your review extension enabled!
Increased CTR on results pages
Correctly formatted reviews can help increase click-throughs from search engine results pages. In the image below, the addition of star ratings make the first and third results stand out.
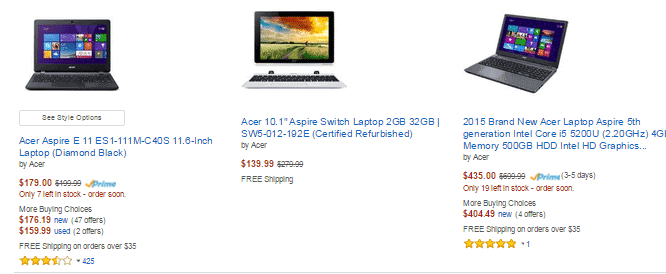
Increased conversion rates
By increasing the chance of a click-through, you’re also increasing the chance for conversion. User reviews can increase trust in your ecommerce site, and can help remove doubts about products.
To collect customer reviews, try the following:
- Email customers a few weeks after purchasing and ask for a review.
- Offer discounts or other incentives on their next purchase in exchange for a review.
Don’t worry about negative reviews. Instead, take it as an opportunity to show good customer service. Offer to replace the faulty product or offer a refund.
2. Pagination
Because e-commerce sites are promoting a variety of products, they´re ultimately forced to divide them into multiple pages. This process is called pagination.
If you have product categories that contain thousands of products, make sure that all of them are indexed and regularly crawled. Google has some good instruction on pagination with rel=“next” and rel=“prev”.
Pagination affects two critical elements of search engine accessibility:
Crawl Depth: Google demands best practices, wherein spiders should reach content-rich pages in as few clicks as possible. If you have too much paginated content, Googlebot won’t travel through all of them. It won’t be able to index the final pages.
Duplicate Content: Search engines want to show only a single URL for a piece of content. If pagination is not implemented correctly, it may cause duplicate content problems. This will cause some confusion for the Googlebot, especially during search queries.
3. Page Speed
Google announced that website speed would begin having an impact on search ranking. Apparently for Google, a poor performing website results in a poor user experience. It’s enough reason for a website to gain less promotion in search results.
A user is not going to wait for your product pages to load, so you should care about site speed. Any delay is enough reason to make your customers leave. This converts to lost revenue, which can hurt your bottom-line.
There are several ways to optimize your WooCommerce site’s speed. You can read all about it here.
4. Search Option
Even with a good navigation structure, there are users who will just prefer to search. That’s why a search box has become an essential element of e-commerce sites.
Using your search feature, you can track your customers’ searches using CMS or Google Analytics. What phrases are they using? Does your site return good results? Is your search function working for singular and plural keywords?
Monitor the number of people who search and then leave straight away. What prevents them to go through the checkout process? Try including special offers related to the search, and see if it lessens your bounce rate. The data you have collected will help you improve your website and customer experience.
5. Product Description
It is very important to make your product descriptions unique. For retailers, don’t just rely on the manufacturer’s brochure. If you do, then you’ll have the same content as hundreds of other retailers. Make it unique and engaging.
Product descriptions shouldn’t just describe your products, product descriptions should sell them.
Here’s how:
Focus on your ideal buyer
If you focus on a huge group of buyers, you may end up addressing no one at all. Imagine your ideal buyer and consider how you would speak to him if you were selling your product face-to-face. Does he appreciate a good humor?
ThinkGeek starts their product description as:
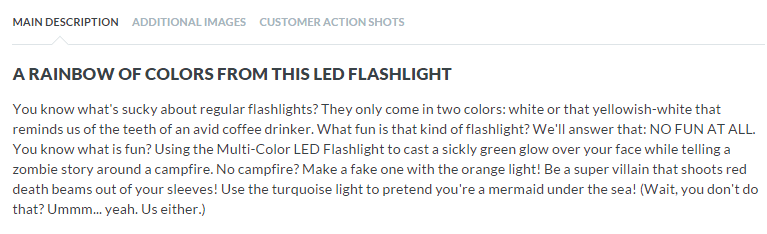
Entice with benefits
A consumer always wants to know what’s in it for them. What are your product’s features and specifications? Know how to highlight the benefits.

Methodhome highlights the powergreen action of their all-purpose cleaner, wherein grease and grime don’t stand a chance!
6. Business Information
To optimize your business information, make sure that it’s complete and accurate.
Phone number: this can actually inspire trust. If a phone number is shown, it gives customers the impression that you can provide customer support if ever they encounter some problems with the purchase.
Company details: this is especially helpful if you’re trying to target local markets. If you give Google some location signals, it can help your location keywords rank.
7. Social Sharing
Are you happy with how social share buttons work on your website? To maximize the benefits, social share buttons need to be optimized.

What’s an optimized share button?
It’s a share button that automatically generates a shareable message with custom information for your brand.
Here’s an example of an optimized Tweet:
Notice that the tweet has the brand’s Twitter handle @jcrew.
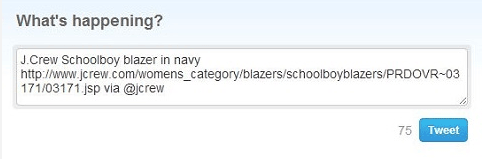
Customizing your share buttons let your readers share useful information, and help you control brand messaging at the same time. You’re making it easy for your visitors to share your products on their social media profiles.
We all know how social media connects people who value each other’s opinions. People who see content being shared by their friends, family, or colleagues will think that it’s something worth checking out. This means more traffic to your site!
You can place social share buttons…
- After the point of purchase on a confirmation type page
- Email follow up and correspondence
- After a review has been published – give the reviewer the option to share their review
V. Conclusion
With these steps, you can start optimizing the pages of your online store. If you want to do this by yourself, there are plenty of SEO tools given in this article to help you optimize your rankings. Nevertheless, don’t be shy to reach out to a professional for help. On the other side of the coin don’t try and outsource this completely, no one understands your products like you; an internal team member with intimate knowledge of the products and target market needs to be involved.
If on-page optimization is done right, you will see an increase in quality traffic, which will lead to more conversions and repeat visitors.
Keep in mind that Google constantly updates their algorithms, which also means you have to be up-to-date with your strategies. It may require a lot of work, but the benefits are worth it.







Leave a Reply